Automation and Robotics: Transforming the Healthcare Journey
Automation and robotics are transforming many industries, and healthcare is no exception. Integrating these technologies into healthcare systems is revolutionising patient care and enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of resource-challenged healthcare professionals. From robotic-assisted surgeries to automated medication dispensers, the advancements in this field are paving the way for a new era in medical care.
At PDD, we take a deep dive into this fast-evolving area to understand the opportunities the technology offers across the care continuum, as well as the barriers to acceptance that threaten to slow its integration.
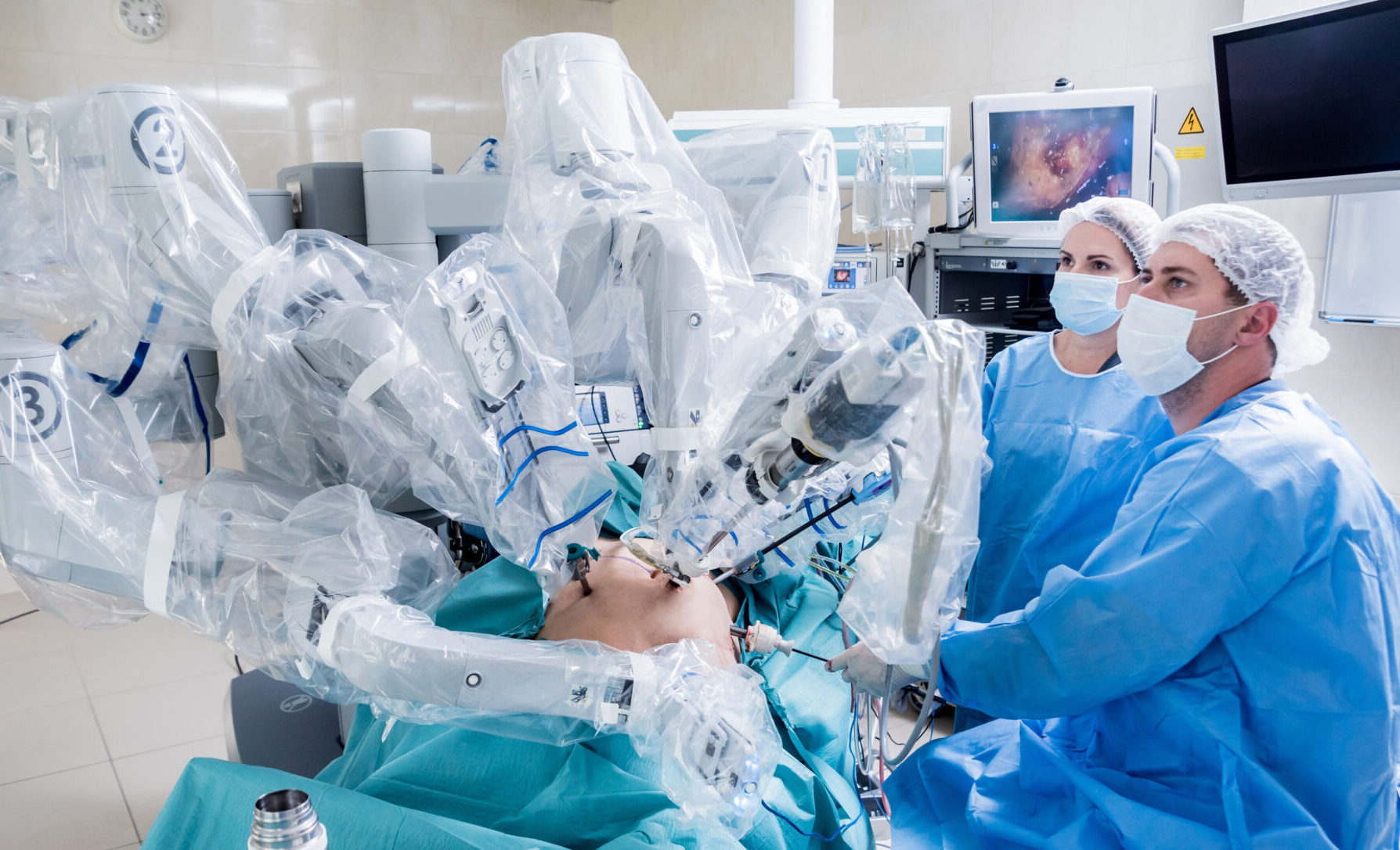
Precision and control: robotic-assisted Surgeries
Robotics have made significant contributions to healthcare, particularly in surgery. In 2023, the global medical robotics market stood at $13.19 billion, and is expected to be worth $52.41 billion by 2032, with hospitals holding the largest market share. Robotic-assisted surgical systems, like the Da Vinci Surgical System, allow surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater precision, flexibility, and control. Providing a magnified, 3D high-definition view of the surgical area, these systems allow for minimally invasive procedures, resulting in smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and quicker recovery times for patients.
Robotic systems also enable telesurgery, where surgeons can perform operations remotely using robotic instruments. This technology has the potential to deliver high-quality surgical care to patients in remote or underserved areas, effectively bridging the gap between healthcare resources and patient needs.
Reducing medication errors with automation
Medication errors are a significant concern in healthcare, often leading to adverse patient outcomes. Automation in medication dispensing tackles this issue by ensuring accurate and timely delivery of medications. Automated medication dispensing systems (AMDS) streamline the medication management process, reducing the risk of errors associated with manual dispensing. These systems can store, track, and dispense medications based on electronic prescriptions, ensuring patients receive the correct dosage at the right time.
Pharmacy robots, another advancement in this area, can prepare and package medications in a sterile environment, minimising the risk of contamination and errors. These robots are particularly beneficial in hospitals with high patient volumes, where manual dispensing can be time-consuming and prone to mistakes.
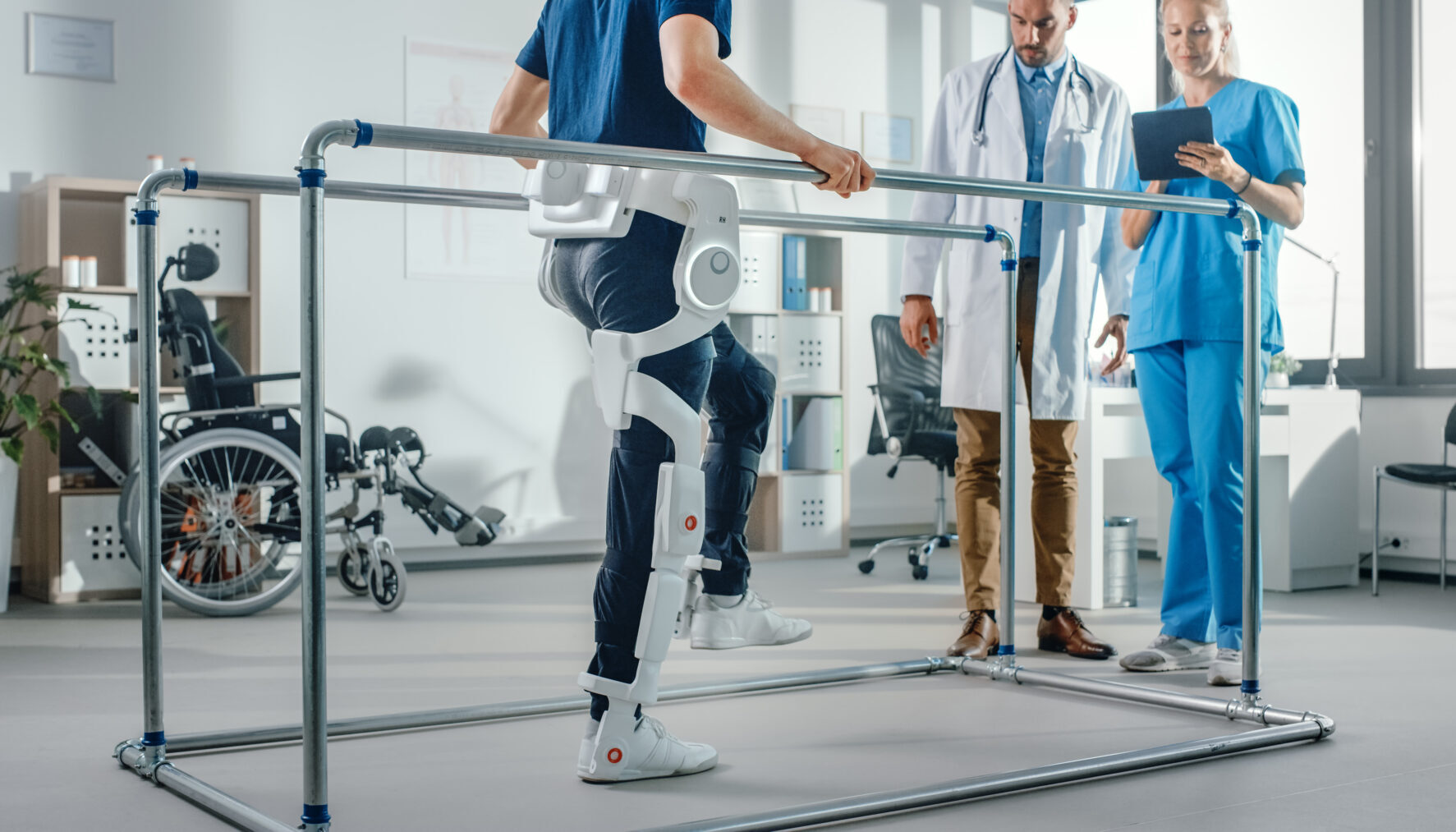
Enhancing recovery through robotic rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is critical to the recovery of patients with neurological disorders, injuries, or post-surgery needs. Robotic rehabilitation devices, such as exoskeletons and robotic limbs, are enhancing the rehabilitation process by providing consistent, repetitive, and precise movements that are essential for recovery. These devices can be tailored to individual patient needs, offering personalised rehabilitation programs.
Robotic exoskeletons are being used to assist patients with spinal cord injuries or those who have suffered a stroke, in regaining mobility. These wearable devices support and enhance the patient’s movements, promoting muscle strength and coordination. The use of robotics in rehabilitation not only accelerates recovery but also improves the overall quality of life for patients.

Remote monitoring: shaping the future of patient care
Automation and robotics are crucial in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. With the rise of telehealth services, patients can now consult with healthcare providers from home. Robotic systems equipped with cameras, screens, and medical instruments can facilitate remote examinations, enabling doctors to assess and diagnose patients without the need for physical presence.
Remote monitoring devices, integrated with automation technology, can track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels. These devices automatically transmit data to healthcare providers, allowing for continuous monitoring of patients with chronic conditions. Early detection of abnormalities through remote monitoring can lead to timely interventions, reducing the risk of complications and hospital readmissions.
Paving the way ahead: barriers and opportunities to adoption
The continuous improvement of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning capabilities will continue drive the development of more intuitive and responsive systems that can anticipate patient needs and enhance decision-making. However, while the benefits of robotics and automation in healthcare are substantial, significant challenges remain to ensure greater acceptance and integration by patients and healthcare professionals.
The high costs of robotic systems and automation technologies are a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in developing countries. Additionally, there is a need for specialised training for healthcare professionals to effectively use these advanced systems.
Data security and patient privacy are also significant concerns, as the integration of these technologies involves the collection and transmission of sensitive health information at scale; therefore, robust cybersecurity measures are crucial to protect patient data from breaches and unauthorised access.
Advancements in technology, combined with ongoing research and development, are expected to enhance the capabilities of robotics and automated systems in healthcare over the coming year. Innovations in this area will become essential if we are to addrƒess the growing demands and complexities of modern healthcare and will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes, reducing healthcare costs, and transforming the overall landscape of medical care.
Embracing a move to greater automation in healthcare will require a concerted effort from all stakeholders to ensure that the technology acts as a complement to the human element of healthcare, enriching patient-provider interactions and setting a new standard for what is possible in the delivery of care.
If you would like to find out how PDD can help you uncover opportunities of automation in healthcare, please get in touch.



